How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, innovative videography, and exciting new perspectives. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced techniques and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the basic controls and navigating different flight modes to mastering camera settings and post-flight maintenance. Safety is paramount, and we’ll emphasize crucial pre-flight procedures and emergency protocols. Furthermore, we’ll delve into the legal and regulatory aspects of drone flying, ensuring you comply with all relevant laws and regulations in your area.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to embark on your aerial adventures with confidence and skill.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying functionality, and assessing environmental conditions. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection covers several critical areas. Battery levels should be checked to ensure sufficient power for the intended flight duration. Propellers should be carefully examined for any damage, cracks, or imbalance. A strong GPS signal is essential for accurate positioning and control; a weak signal may result in erratic flight behavior or loss of control.
Furthermore, the overall physical condition of the drone should be assessed for any visible damage.
Pre-Flight Safety Checklist
The following checklist summarizes the essential steps for a thorough pre-flight safety check. Following this procedure consistently will significantly reduce the risk of incidents.
| Item | Check | Notes | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge? | Check voltage and remaining flight time. | Replace if necessary. Charge fully before next flight. |
| Propellers | Damage, cracks, or imbalance? | Inspect each propeller carefully. | Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal | Strong signal? | Observe the number of satellites locked. | Relocate to an area with better signal if necessary. |
| Gimbal | Properly calibrated and functioning? | Check for smooth movement and proper alignment. | Recalibrate if needed. |
| Drone Body | Any damage or loose parts? | Inspect the entire drone for physical damage. | Repair or replace damaged parts. |
| Flight Environment | Safe and legal airspace? | Check for obstacles, weather conditions, and airspace restrictions. | Postpone flight if conditions are unsafe or illegal. |
Emergency Procedures, How to operate a drone
Knowing how to respond to emergencies is paramount. In the event of a signal loss, most drones are equipped with a Return-to-Home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point. However, understanding the specific RTH capabilities of your drone model is essential. If a malfunction occurs, attempt to safely land the drone, prioritizing the safety of people and property.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering in different environments, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident and responsible drone operator. Remember consistent practice is key to mastering the skills needed for safe and effective drone operation.
Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Successfully operating a drone requires understanding its control system and navigation capabilities. This section will guide you through the basic functions of a drone controller and provide tips for safe and controlled operation.
Drone Controller Functions
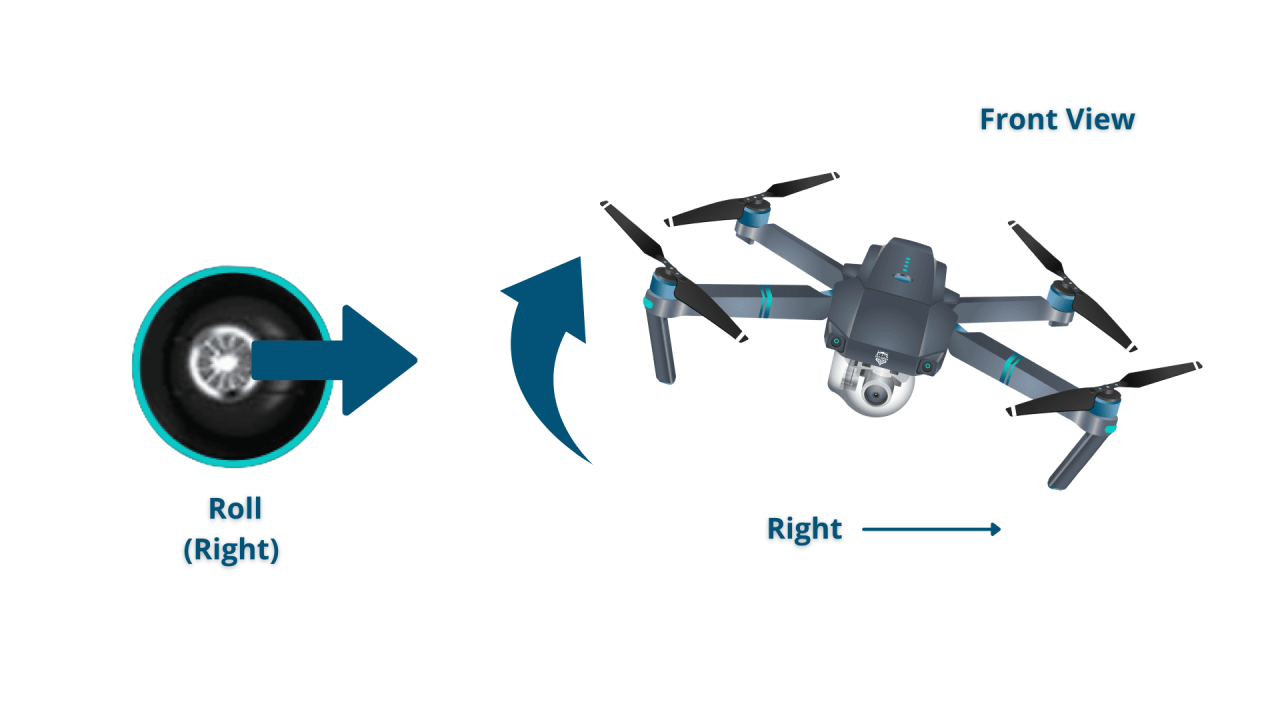
Most drone controllers utilize four primary control sticks: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. The throttle controls the drone’s altitude (up and down). Yaw controls the drone’s rotation (left and right). Pitch controls the drone’s forward and backward movement. Roll controls the drone’s left and right lateral movement.
Understanding these functions is fundamental to safe drone operation.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are crucial for precise drone navigation. The calibration process typically involves a series of movements instructed by the drone’s software. This ensures the drone accurately understands its orientation and location, preventing erratic flight patterns. The specific steps vary depending on the drone model and its software, so consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions.
Tips for Smooth Drone Operation
Smooth and controlled operation comes with practice. Avoid abrupt movements of the control sticks, especially during takeoff and landing. Maintain a consistent speed and altitude, adapting your control inputs to the drone’s responsiveness. Pay close attention to the drone’s visual feedback and adjust your movements accordingly.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure
The following steps provide a safe and reliable takeoff and landing procedure. Always perform a pre-flight check before initiating takeoff.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Once airborne, maintain a stable altitude and position.
- For landing, slowly decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Flight Modes and Settings
Modern drones offer various flight modes and settings that cater to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Understanding these options is key to maximizing your drone’s capabilities while maintaining safety.
Flight Mode Descriptions
Different flight modes provide varying levels of control and stability. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, making it ideal for novice pilots. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots. Other modes, such as GPS mode, RTH mode, and follow-me mode, offer specialized functionality. The specific modes and their features vary between drone models.
Adjusting Flight Settings
Adjusting flight settings allows customization of the drone’s behavior. Maximum altitude limits the drone’s vertical ascent, preventing it from flying too high. Maximum speed controls the drone’s horizontal velocity. Return-to-home (RTH) settings define the drone’s behavior in case of signal loss or low battery. These settings are typically adjusted through the drone’s mobile application or control software.
Flight Mode Comparison
The suitability of a flight mode depends heavily on the pilot’s skill level, the environment, and the intended task. Beginner mode is ideal for learning the basics, while sport mode is suited for more advanced maneuvers. GPS mode enhances stability, especially in windy conditions. Understanding the trade-offs between stability, control, and maneuverability is important when selecting a flight mode.
| Flight Mode | Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limited speed and responsiveness, enhanced stability | Reduced maneuverability |
| Sport Mode | High speed and responsiveness, increased maneuverability | Requires more skill and control |
| GPS Mode | Improved stability and positioning accuracy | May require a strong GPS signal |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) Mode | Automatic return to home point | Relies on GPS signal and battery level |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of most drones, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for capturing high-quality content.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive tutorials and tips. Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice, but with proper guidance, you’ll soon be navigating the skies with confidence.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture significantly impact image quality. ISO controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Shutter speed determines the duration of light exposure. Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens. Adjusting these settings allows for control over brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
Experimentation is key to mastering these settings.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
High-quality aerial photos and videos require careful planning and execution. Consider lighting conditions, composition, and subject matter. Smooth, controlled movements are crucial for avoiding blurry images. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique and compelling shots. Post-processing can further enhance the final product.
Using Camera Features
Most drone cameras offer features like zoom, focus, and various shooting modes. Understanding how to utilize these features effectively can significantly enhance the quality and creativity of your aerial footage. For example, zoom allows for close-up shots, while focus controls the sharpness of the subject.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots
Effective aerial composition involves understanding the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Utilize the drone’s maneuverability to create visually appealing shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find unique compositions. Consider the surrounding environment and incorporate it into your shots to create a sense of place.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance

Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation.
Securing the Drone After Flight
After each flight, carefully secure the drone. Power it down completely, and store it in a safe, dry location, preferably in its protective case. Inspect the drone for any damage or debris and clean it as needed. Ensure the battery is properly stored to prevent damage.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are vital for the long-term performance and reliability of your drone. This involves inspecting the propellers, motors, and gimbal for any signs of wear and tear. Clean the drone body and camera lens to remove dust and debris. Proper maintenance will prevent unexpected malfunctions and extend the drone’s operational life.
Maintenance Schedule

- Daily: Inspect propellers and body for damage.
- Weekly: Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Monthly: Inspect motors and gimbal for wear and tear.
- Quarterly: Perform a thorough inspection of all components.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Common drone problems include battery issues, motor malfunctions, and GPS signal problems. Understanding the causes and troubleshooting steps for these problems can prevent major issues. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting instructions. In some cases, professional repair may be necessary.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. Understanding these regulations is crucial to avoid legal penalties and ensure safe and ethical drone operation.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary by location. Before flying, research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area. This typically involves registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and adhering to airspace restrictions. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines or legal action.
Airspace Restrictions
Airspace restrictions designate areas where drone flight is prohibited or restricted. These restrictions may be in place for safety reasons, to protect sensitive infrastructure, or to prevent interference with other aircraft. Before each flight, consult official sources such as the FAA’s B4UFLY app (for the USA) or equivalent resources in your country to check for airspace restrictions.
Privacy and Unauthorized Surveillance
Respecting privacy and avoiding unauthorized surveillance is paramount. Never fly your drone over private property without permission. Avoid recording individuals without their consent. Be mindful of the ethical implications of drone usage and ensure your actions comply with all privacy laws and regulations.
Summary of Key Legal Regulations
- Register your drone (where required).
- Obtain necessary permits or licenses.
- Adhere to airspace restrictions.
- Respect privacy and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, exploring advanced drone techniques can unlock new creative possibilities and operational capabilities.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as circling, orbiting, and waypoint navigation require precise control and understanding of the drone’s capabilities. Circling involves maintaining a consistent radius around a point. Orbiting involves following a circular path around a subject. Waypoint navigation allows for pre-programmed flight paths, enabling complex aerial shots and surveys.
Advanced Flight Features
Advanced flight features such as follow-me mode and point-of-interest (POI) mode automate certain flight tasks. Follow-me mode allows the drone to automatically track a moving subject. POI mode allows the drone to orbit a designated point of interest. These features simplify complex shots and free up the pilot’s attention.
Planning Complex Drone Flights
Planning complex drone flights involves careful consideration of the flight path, airspace restrictions, battery life, and environmental conditions. Utilizing flight planning software can greatly assist in this process, allowing for visualization and optimization of the flight route.
Sample Flight Plan
A sample flight plan might involve taking off from a designated point, ascending to a pre-determined altitude, then flying along a predefined path using waypoints, capturing aerial images at specific points, and finally returning to the starting point for landing. This plan would need to take into account factors such as wind conditions and the drone’s battery life. The path could be visualized as a series of connected points on a map, with each point representing a waypoint with specific altitude and camera settings.
The drone would autonomously navigate between these waypoints, following the planned route.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey, combining technological prowess with a keen sense of responsibility. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the satisfaction of capturing breathtaking aerial footage, the experience is both exhilarating and enriching. By following the guidelines and safety procedures Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of your drone, creating stunning visuals and expanding your creative horizons while always prioritizing safe and responsible flight practices.
Remember to continuously update your knowledge on regulations and best practices to ensure your continued safe and legal operation.
User Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automated return-to-home functions. Look for models with intuitive controls and good crash resistance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (e.g., hovering vs. high-speed flight), and weather conditions. Typically, you can expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes per battery.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point. If your drone doesn’t have RTH, attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, carefully search the area.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures in your area.
