China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News – that headline alone sparks a lot of conversation. This piece dives into how China became a global manufacturing giant, exploring its strengths, weaknesses, and the huge impact it has on the world economy. We’ll look at its history, the policies that fueled its growth, and the challenges it faces today, from rising labor costs to geopolitical tensions.
Get ready for a fascinating look at a truly global powerhouse.
We’ll trace China’s manufacturing journey, from its early days to its current dominance, highlighting key moments and government initiatives. We’ll also examine its competitive advantages – things like low labor costs and extensive infrastructure – and the technological advancements driving its success. But we won’t shy away from the challenges. We’ll discuss issues like environmental concerns, intellectual property rights, and the impact of trade wars.
Finally, we’ll speculate on the future of Chinese manufacturing and its ongoing influence on global markets.
China’s Manufacturing Powerhouse

China’s ascension as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, it has evolved into a global manufacturing giant, impacting industries, economies, and consumers worldwide. This exploration delves into the historical context, strengths, challenges, and future prospects of Chinese manufacturing, examining its global impact and influence.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s journey to manufacturing dominance is a multi-decade process shaped by strategic policy decisions and significant historical events. This section traces that evolution, comparing it to the growth trajectories of other manufacturing powerhouses.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking. It’s all about seizing the right moment, just like in hockey, check out this article on Jonathan Toews’s future Why timing is key consideration in potential Jonathan Toews NHL to see what I mean. The parallels are surprising; China’s global influence, much like a star player’s career arc, hinges on perfect timing and strategic moves.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms initiated by Deng Xiaoping | Opened China to foreign investment and market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for rapid industrial growth. | Significant increase in foreign direct investment (FDI) and export growth in the following decades. |
| 1980s-1990s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted foreign investment and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | Rapid growth of manufacturing hubs like Shenzhen and Zhuhai. |
| 2001 | Accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global trading system, boosting exports and attracting more foreign investment. | Substantial increase in trade volume with other WTO members. |
| 2010s-Present | Focus on technological advancement and domestic consumption | Shift towards higher-value manufacturing and reduced reliance on low-cost labor. | Increased investment in R&D and growth of domestic brands in various sectors. |
Strengths of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
China’s manufacturing prowess rests on several key pillars: low labor costs, extensive infrastructure, robust supply chains, and significant government support. These factors have enabled Chinese manufacturers to achieve remarkable scale and efficiency.
- Low Labor Costs: Historically, China’s large and relatively low-cost labor pool provided a significant competitive advantage in labor-intensive manufacturing.
- Extensive Infrastructure: Massive investments in infrastructure, including transportation networks and energy grids, facilitated efficient production and distribution.
- Robust Supply Chains: A highly integrated and efficient domestic supply chain ecosystem enables cost-effective production and rapid scaling of operations.
- Government Support and Industrial Policy: Targeted government policies, including subsidies, tax incentives, and infrastructure development, have played a crucial role in fostering manufacturing growth.
- Technological Capabilities: While initially reliant on low-cost labor, China has made significant strides in technological capabilities across various sectors, including electronics, renewable energy, and high-speed rail.
Companies like Huawei, Xiaomi, and BYD exemplify the success of Chinese manufacturers in global markets, demonstrating technological prowess and competitive pricing strategies.
That Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is a wild ride! It really highlights how deeply intertwined global supply chains are with China, and you can see the discussion for yourself by checking out this link: China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. The sheer scale of their production is mind-boggling, and the article explores the implications of that fact.
So, if you’re interested in global economics and manufacturing, definitely give that Hacker News thread a read.
Challenges Faced by Chinese Manufacturing
Despite its remarkable success, China’s manufacturing sector faces significant challenges that threaten its continued dominance. These include rising labor costs, environmental concerns, technological competition, and geopolitical factors.
- Rising Labor Costs
- Environmental Concerns and Regulations
- Technological Competition from other nations
- Trade Wars and Geopolitical Tensions
- Intellectual Property Rights Concerns
Potential solutions include investing in automation and AI, fostering innovation and technological advancement, strengthening intellectual property protection, and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
The Future of Chinese Manufacturing
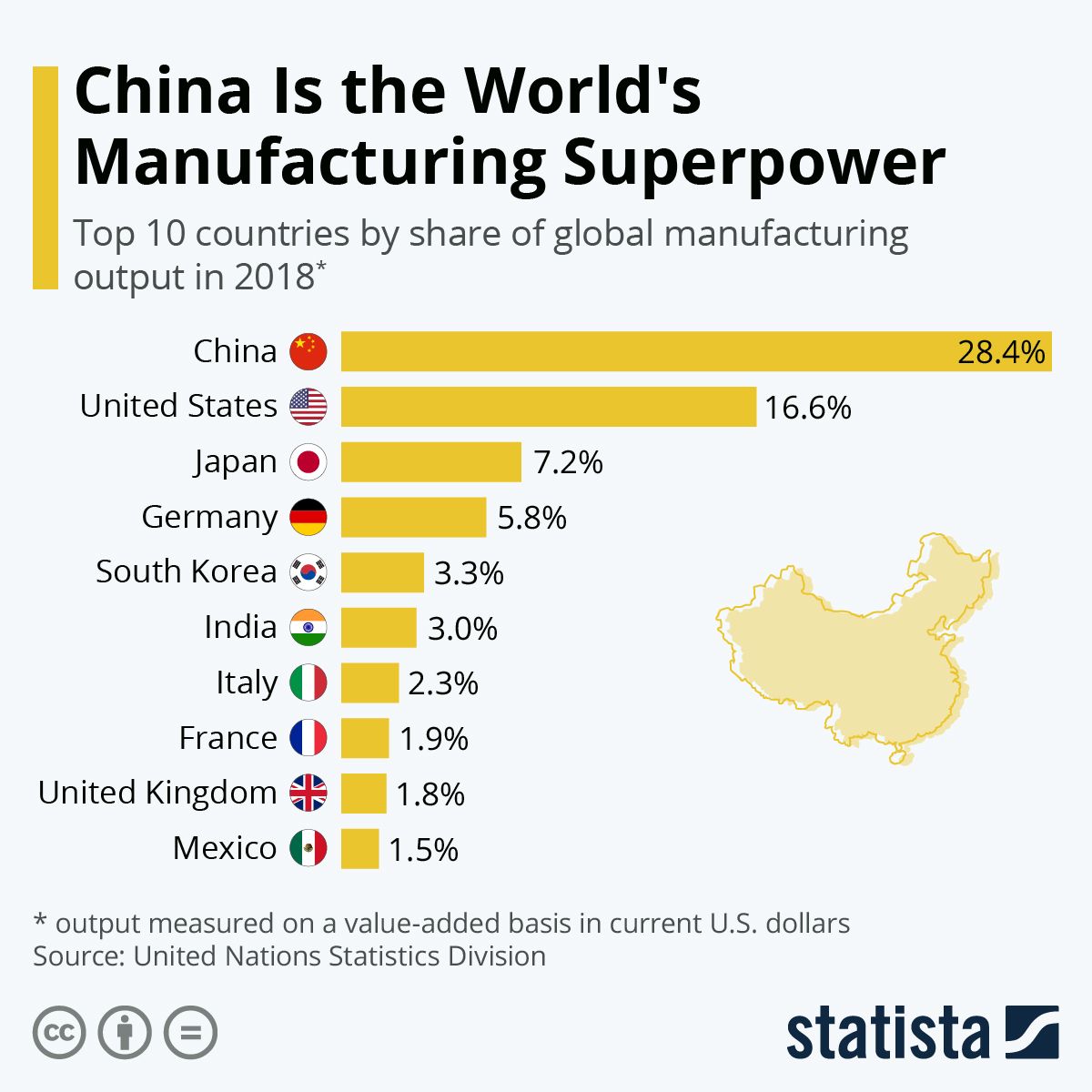
The future of Chinese manufacturing will be shaped by several key trends, including automation, AI, shifting global supply chains, and the rise of regional manufacturing hubs. These factors will influence China’s ability to maintain its competitive edge.
One potential scenario sees China focusing on higher-value manufacturing, leveraging AI and automation to enhance productivity and compete on technology and innovation, rather than solely on cost. This shift could involve a move towards more specialized and technologically advanced manufacturing sectors, potentially reducing reliance on labor-intensive industries.
Impact on Global Manufacturing

China’s manufacturing dominance has profoundly impacted global economies, international trade, and consumer markets. This section compares the impact on various economies and analyzes its implications for international competition.
| Country | Strengths | Weaknesses | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Large and skilled workforce, robust infrastructure, complete supply chains | Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, technological dependence in some sectors | Continued growth in high-value manufacturing, increased automation and AI adoption |
| United States | Strong technological innovation, high skilled labor, large domestic market | High labor costs, reliance on imports for some goods | Focus on reshoring and technological advancement, potential for increased manufacturing competitiveness |
| Germany | High-quality manufacturing, strong engineering expertise, advanced automation | High labor costs, reliance on exports | Continued focus on high-value manufacturing and technological leadership |
Illustrative Examples of Chinese Manufacturing Influence
The influence of Chinese manufacturing is evident across numerous product categories. This section provides detailed examples to illustrate its global reach and impact.
Consider the smartphone industry. A vast majority of smartphones globally utilize components manufactured in China, highlighting the country’s dominance in electronics manufacturing. The production process involves a complex supply chain, with numerous Chinese companies specializing in different aspects of smartphone production, from component manufacturing to assembly. This has led to significant cost reductions and increased availability of smartphones globally.
A major Chinese manufacturing company like Foxconn, known for its vast manufacturing operations and global reach, plays a significant role in assembling electronics for many international brands. Its intricate supply chain, efficient production capabilities, and global network exemplify the scale and impact of Chinese manufacturing.
The rise of 5G technology, with significant contributions from Chinese companies like Huawei, illustrates the impact of technological advancements originating from or significantly impacting Chinese manufacturing. The development and deployment of 5G infrastructure have influenced global telecommunications networks and technological innovation across various sectors.
Final Summary: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a complex story, one marked by both remarkable achievements and significant challenges. While its dominance is undeniable, the future remains uncertain. Factors like automation, shifting global supply chains, and geopolitical instability will all play crucial roles in shaping the next chapter. Understanding China’s manufacturing landscape is essential for anyone involved in global trade, economics, or technology, and this overview provides a solid foundation for further exploration.
Answers to Common Questions
What are some examples of specific products heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing?
Electronics (smartphones, computers), textiles and clothing, toys, and many consumer goods are heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of medical devices, even those used in surgery, are likely made there. If you’re interested in becoming a surgical tech, you’ll need to meet specific program requirements, so check out the admission details here: surgical tech program admission requirements and prerequisites. Understanding this process is key, especially considering the global supply chains involved, many of which originate from China’s massive manufacturing sector, as highlighted in that Hacker News article.
How does China’s manufacturing sector impact consumer prices globally?
Generally, Chinese manufacturing keeps prices lower due to its scale and efficiency, but this can be offset by tariffs and transportation costs.
What are the biggest threats to China’s continued manufacturing dominance?
Rising labor costs, automation in other countries, trade wars, and geopolitical instability are all potential threats.
Is China focusing on moving up the value chain in manufacturing?
Yes, China is actively investing in higher-value manufacturing, such as advanced technology and automation, to reduce its reliance on low-cost labor.
